Table of Contents
Coronavirus Definition
Coronavirus is a family of diseases that can reason illnesses such as the common cold, serve acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), and Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS).
In 2019, an original identify as the source of an illness outbreak that originated in China. This virus is now known as simple acute respiratory pattern coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).
The disease it sources is called coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). In March 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) professed this COVID-19 outbreak to be an epidemic.
These groups have also published recommendations to prevent and treat this disease.
What are the Symptoms of Coronavirus?

Signs and indications of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) can appear between two and 14 days after exposure to the virus.
This period between exposure and before the onset of symptoms is called the incubation period.
The most common signs and symptoms may include:
- Fever
- Cough;
- Fatigue;
- The first symptoms of COVID-19 may include loss of taste or smell.
Other symptoms can include:
- Shortness of breath or trouble breathing;
- Muscle aches;
- Shaking chills;
- Sore throat;
- Runny nose;
- Headache;
- Chest pain;
- Conjunctivitis.
This list does not include all thinkable signs and symptoms—other less common symptoms report, such as a skin rash, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Children have symptoms like those of adults and generally have a mild illness.
The severity of COVID-19 signs can range from very mild to extreme. Some people may have only a few characters, and others may not have any.
In some people, symptoms may worsen, such as more trouble breathing and pneumonia, about a week after starting. If you have any of the above symptoms check yourself covid tested. Covid 19 testing is a type of blood test that helps detect Coronavirus, a serious respiratory infection. Despite the availability of this type of testing, coronaviruses are still relatively rare and they typically pass on without many people knowing because so few tests are performed. People who already have chronic health situations may also be at higher risk of becoming seriously ill.
Certain health conditions that increase your danger of becoming seriously ill with COVID-19 include:
- Serious heart diseases, such as heart disaster, coronary artery disease, or cardiomyopathy;
- Cancer;
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD);
- Type 2 diabetes;
- Obesity, or severe obesity;
- Smoke;
- Chronic kidney disease;
- Sickle cell disease;
- It weakened the immune system from a solid organ transplant.
Other conditions, such as: can increase the risk of more severe disease:
- Asthma;
- Liver disease;
- Overweight;
- Chronic lung illnesses, such as cystic fibrosis or pulmonary fibrosis;
- Brain and nervous system conditions;
- The weakened immune system from bone marrow transplant, HIV, or some medications;
- Diabetes type 1;
- High blood pressure.
What are the Causes of Coronavirus?
- Infection with the new it(severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, or SARS-CoV-2) causes coronavirus disease 2019 ( COVID-19 ).
- The virus that reasons COVID-19 spreads quickly from person to person and more continues to discover over time about how it applies.
- The data shows that it mainly spread from person to person among those in close contact (within about 6 feet, or 2 meters).
- The virus spread by respiratory droplets released when someone with the virus coughs, sneezes, or talks.
- A nearby person may inhale these droplets, or the droplets may land in their mouth, eyes, or nose.
- In some situations, the virus that causes COVID-19 can spread when a person exposes to tiny droplets or aerosols that continue in the air for several minutes or hours.
- It is known as airborne transmission—it did not yet know whether it is common for the virus to transmit by this means.
- It can also feast when a person touches a surface or object where the virus finds then touches their mouth, nose, or eyes, although this does not consider the main ways it spread.
- There have been a few belongings of reinfection with the virus that causes COVID-19, but it has been rare.
Risk Factors of Coronavirus
Risk factors for COVID-19 appear to include:
- Close interaction (less than 6 feet or 2 meters) for more than 5 minutes with someone who has COVID-19,
- An infected person is coughing or sneezing very close to you.
Complications of Coronavirus
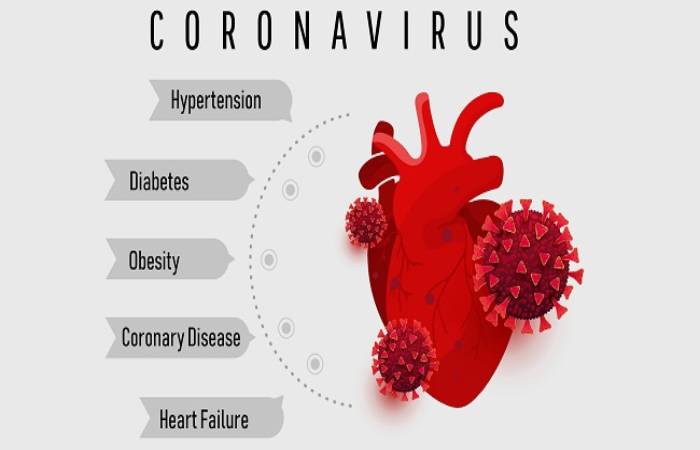
Although most people with COVID-19 have slight to moderate indications, the disease can lead to serious medical complications and, in some people, cause death.
Older adults or people with chronic situations are at a higher risk of becoming seriously ill with COVID-19.
Some of the complications can include:
- Pneumonia and trouble breathing;
- Failure of various organs;
- Heart problems;
- A lung condition that causes too little oxygen to pass through the bloodstream to organs (acute respiratory distress syndrome);
- Blood clots;
- Acute kidney injury;
- Other viral and bacterial infections.
Prevention of Coronavirus
Even if there is no vaccine to prevent COVID-19, you can take steps to reduce your risk of infection.
WHO and CDC commend taking these precautions to avoid exposure to the virus that causes COVID-19 :
- Avoid close interaction (less than 6 feet or 2 meters) with anyone who is tasteless or exhibiting symptoms.
- Keep the distance between yourself and others (6 feet or 2 meters). It is imperative if you are at higher risk for a severe illness.
- Be aware that some persons can have COVID-19 and spread it to others, even if they don’t have indications or distinguish they have COVID-19.
- Rinse your hands repeatedly with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, or use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer covering at least 60% alcohol.
- Shelter your face with a cloth mask once you are in community places, such as the grocery store or supermarket, where it is challenging to avoid close contact with others.
- If there are surgical masks, you can use them. N95 respirators should reserve for healthcare workers.
- Protection of your mouth and nose with your elbow or material when you cough or sneeze. Dispose of the used tissue. Wash your hands immediately.
- Avoid moving your eyes, nose, and mouth.
- Avoid allotment dishes, glasses, towels, bedding, and other domestic items if you are tasteless.
- Clean and sanitize regularly touched surfaces, such as door latches, light switches, electronics, and countertops daily.
- Stay home and do not drive to work, school, or public places if you are sick unless receiving medical attention. Avoid public transportation, taxis, and rideshare if you are sick.
Travels
- If you are planning to travel, first check the CDC and WHO websites for updates and tips.
- Be prepared to dress in a mask and practice proper hand hygiene when in public.
- You may also want to speak with your doctor if you have health conditions that make you more vulnerable to respiratory infections and complications.
Diagnosis of Coronavirus
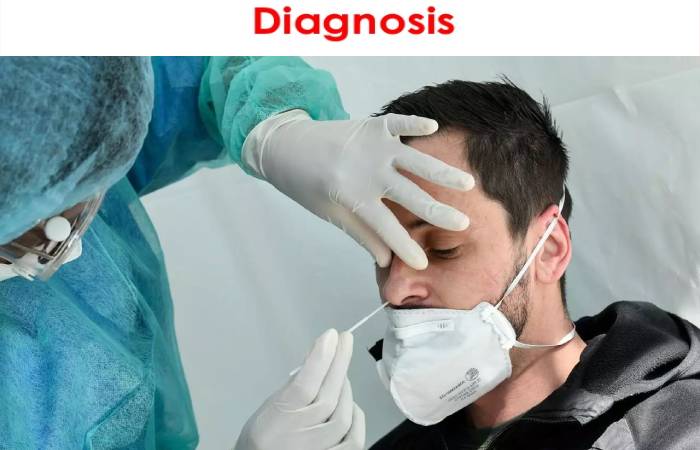
- If you have symptoms of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) or expose to the COVID-19 virus, contact your doctor.
- Also, tell them if you have been in close contact with someone diagnosed with COVID-19.
- The factors used to decide to get tested for the virus that causes COVID-19 can vary depending on your life.
- Conditional on where you are, you may want to have a preliminary examination by your clinic to determine if the test is suitable and if it is available.
- A doctor will determine whether to test for the virus causes COVID-19 based on your signs and symptoms, and you have been in close contact with someone analyzed with COVID-19.
- Your doctor may also reflect testing if you are at higher risk for a severe illness or having a medical procedure.
- To detect the virus that causes COVID-19, a healthcare provider takes a swab from the nose (nasopharyngeal swab) or throat.
- The samples then lead to a laboratory for analysis.
- If you are coughing up sputum, that sample can also send to the lab for analysis.
- The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) takes authorized home testing for the virus that causes COVID-19.
- They can only obtain a prescription from your doctor.
Treatments of Coronavirus
- Right now, there is only one drug approved to treat COVID-19. There is no cure available for COVID-19.
- Antibiotics are not effective in counter to viral infections like COVID-19. Researchers are testing a variety of potential treatments.
- The FDA has accepted the antiviral drug redeliver (Veklury) to treat COVID-19 in adults and children 12 years and older who admit to the hospital.
- The FDA has authorized the drug Baricitinib (Olumiant) emergency use for rheumatoid arthritis to treat COVID-19 in some cases.
- Baricitinib is a pill that appears to work against COVID-19 because it reduces inflammation and has antiviral activity.
- It uses for people who are at increased risk of serious illness from COVID-19.
- This plasma uses to treat people who are seriously ill with COVID-19 in the hospital.
- Supportive medical care aims to relieve symptoms and may include:
- Pain relievers (ibuprofen or acetaminophen)
- Syrup or cough medicine
- Repose
- Fluid intake
9. There is no signal that ibuprofen, or other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines, should avoid.
10. If you have minor symptoms, your doctor may mention that you recover at home.
11. He or she can give you different instructions to control symptoms and prevent spreading the disease to others.
12. She will probably ask you to isolate yourself as much as possible from family and pets while you are sick, to wear a mask when around other people and pets, and to use a separate bedroom and bathroom.
13. Your doctor will likely recommend that you remain in isolation at home for some time, except for medical care.
14. Your doctor will likely monitor you regularly.
15. Follow your doctor and local health department guidelines on when you can end isolation at home.
16. And also, If you are very sickening, you may need treatment in the hospital.
When to See the Doctor
If you have COVID-19 or contact someone diagnosed with COVID-19, contact your doctor or clinic immediately for advice.
Before going to your appointment, talk to your healthcare team about your symptoms and possible exposure to the coronavirus virus.
If you have signs and indications of COVID-19 that indicate an emergency, seek medical attention immediately.
Signs and symptoms that indicate an emergency may include:
- Trouble breathing
- Persistent chest pain or tightness
- Inability to stay awake.
- New confusion
- Bluish-colored lips or face
Suppose you have signs or warning signs of COVID-19, communicate with your doctor or clinic for advice. Tell your doctor if you have other chronic health conditions. And also, Such as heart or lung disease. During the pandemic, it is vital to safeguard medical care for those who need it most.
Conclusion
At this point, there’s no vaccine to protect you from the novel coronavirus, also known as SARS-CoV-2. There also are no particular medications approved to extravagance the symptoms of COVID-19.
However, researchers around the world are at work hard to develop potential vaccines and conduct.
There’s an emerging indication that some medications may have the potential to treat the symptoms of COVID-19.
More large-scale testing needs to regulate if these actions are safe. Clinical trials for these drugs might take several months.
Also Read: Walking – Definition, Benefits, Characteristics, and More
- READ MORE:- fitnessaesthe