Table of Contents
Liver Disease Definition
Liver disease can be inherited (genetic). It can also cause by various factors that damage the liver, such as viruses, alcohol use, and obesity.
The liver is an organ about the size of a soccer ball. It is located just below the rib cage on the right side of the abdomen.
And also, the liver is essential for digesting food and removing toxic substances from the body.
Over time, conditions that damage the liver can lead to scarring (cirrhosis), causing liver failure, a life-threatening situation. But early treatment can give the liver time to heal.
What are the Symptoms of Liver Disease?
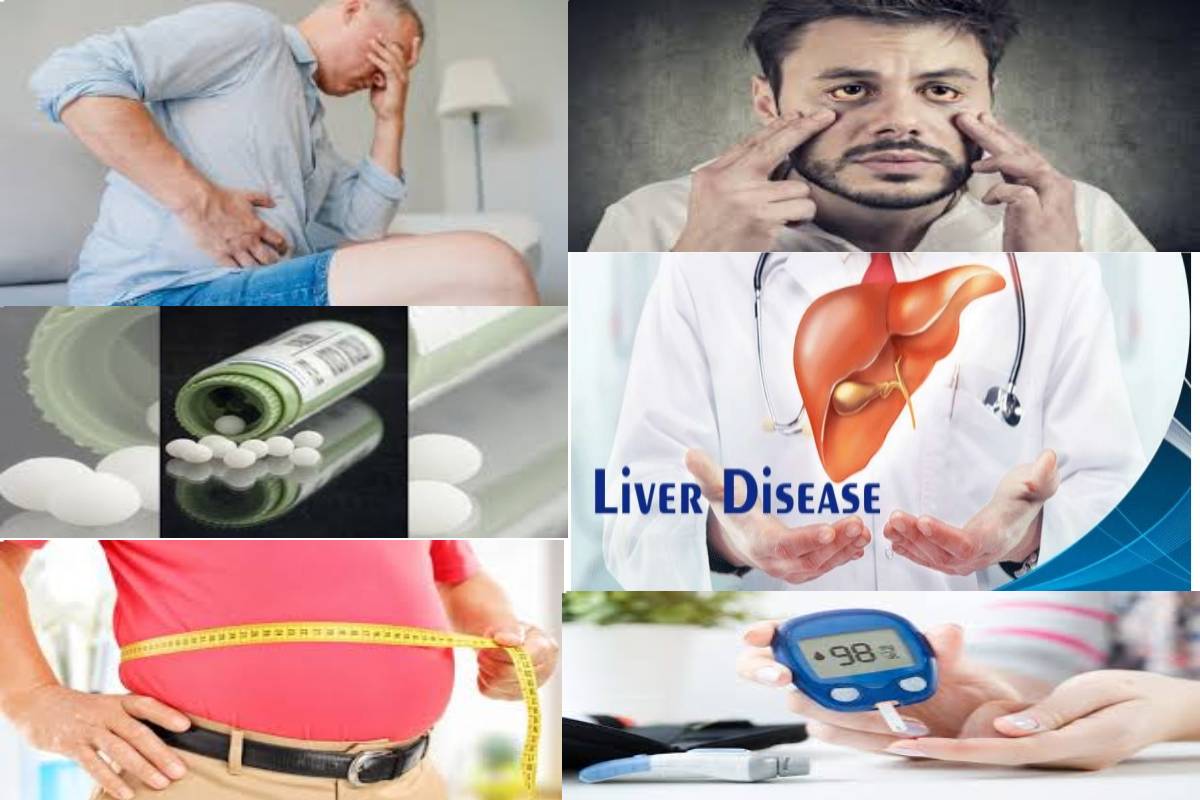
Liver disease doesn’t always cause noticeable signs and symptoms. If signs and symptoms of liver disease are present, they may include the following:
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice)
- Bloating and abdominal pain
- Swelling in the legs and ankles
- Skin itch
- Dark-coloured urine
- The pale colour of stools
- And also Chronic fatigue.
- Nausea or vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Jaundice
- And also, the tendency to bruise easily.
What are the Causes of Liver Disease?
Liver disease has many causes.
1. Infection
Parasites and viruses can infect the liver, causing inflammation that reduces liver function. Viruses that cause liver injury can transmit through contaminated Blood or semen, water or food, or close contact with an infected person. The most common types of liver infection are hepatitis viruses and include:
- Hepatitis A, B
- And also, Hepatitis C.
2. Anomaly in the Immune System
Diseases in which the immune system attacks certain parts of the body (autoimmune) can affect the liver. Examples of autoimmune liver diseases include:
- Autoimmune hepatitis
- Primary biliary cholangitis
- And also, primary sclerosing cholangitis
3. Genetics
An abnormal gene inherited from one or both parents can cause various substances to build up in the liver, causing liver damage. Genetic liver diseases include:
- Hemochromatosis
- Wilson disease
- And also, Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency
4. Cancer and Other Tumors
For example:
- Liver cancer
- Bile duct cancer
- And also, liver adenoma
5. Others
Here are other common causes of liver disease:
- Chronic alcohol abuse
- Fat accumulation in the liver (nonalcoholic fatty liver disease)
- Specific prescription or over-the-counter medications
- And also, certain herbal compounds
What are the Types of Liver Diseases?
Next, we will analyze the significant liver diseases, presenting both their causes and symptoms and the associated treatments.
1. Viral Hepatitis
- By viral hepatitis, we understand any liver inflammation due to colonization of the liver by one of the viruses responsible for hepatitis. A, B, C, D, and E.
- Causes depend on the virus, although they include faecal-oral transmission (consumption of food contaminated with faeces from sick people) or contact with blood or body fluids.
- And also, the severity depends on the causative virus.
- However, symptoms generally consist of abdominal pain, jaundice (yellowing of the skin), fatigue, nausea and vomiting, dark-coloured urine, joint pain, discomfort in the abdominal area, loss of appetite, intense itching the skin.
- Viral hepatitis usually resolves without significant complications after a few weeks without the need for treatment, although in the case of hepatitis B, those affected will need lifelong treatment.
- However, the most severe cases of viral hepatitis may require a liver transplant.
2. Liver Cancer
- With its 840,000 new cases diagnosed each year, liver cancer is the seventh most common cancer globally.
- It consists of forming a malignant tumour in the hepatocytes, and it knows that a significant risk factor is having suffered from viral hepatitis in the past.
- However, it also appears in people who have never had liver disease, in which case the causes are not they are too light.
- Excessive alcohol consumption, family history, and diabetes are other of the most common risk factors.
- Liver cancer does not show symptoms until the liver involvement is excellent, at which point jaundice, weight loss, whitish stools, abdominal pain, vomiting, weakness and fatigue, loss of appetite, etc. are observed.
- Treatment will consist of, depending on the nature of cancer and the person’s health, surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or a combination of several.
- Although many times it is necessary to perform a liver transplant, which, with its 130,000 euros in cost and the more than 12 hours required to carry it out, is one of the most expensive procedures in the world of surgery.
3. Cirrhosis
- Cirrhosis is a chronic disease that appears when there is too much scar tissue in the liver due to alcohol excesses or hepatitis.
- These scars appear when the liver tries to recover from injuries and, if they accumulate, they can make it difficult for this organ to fulfil its functions.
- This situation has the same symptoms as the previous disorders, and the damage is irreversible.
- However, suppose it detects in the early stages. In that case, measures can take (lifestyle change or pharmacological treatments) that slow down the disease’s progress to avoid resorting to a liver transplant.
4. Fatty Liver Disease
- As its name indicates, this liver disease consists of an accumulation of fat in the liver, a situation that, as happened with cirrhosis, hinders this organ’s average performance.
- Its most common cause is excessive alcohol consumption, although there are other triggers as well.
- It has obesity, diabetes, hypertension, very rapid weight loss, liver infections, metabolic disorders, high cholesterol levels.
- All these situations can cause the liver to accumulate more fat than it should. And it is more common than it seems.
- And also, it estimates up to 25% of the population suffers from this problem in a more or less severe way.
- In any case, in the vast majority of cases, the involvement is so small that there are no symptoms.
- These appear in the most severe cases. If lifestyle changes do not work, it may be necessary to undergo medical treatments and undergo a transplant in maximum liver damage.
5. Hemochromatosis
- Hemochromatosis is a disease of genetic and hereditary origin in which the affected person absorbs more iron than the body needs.
- It causes an excess of this mineral, which, to prevent it from circulating freely through the Blood, accumulates, to the heart and pancreas, in the liver.
- This excess iron in the liver compromises its functionality.
- As the accumulation progresses, liver failure may develop, an irreversible clinical condition that can only solve by performing a liver transplant.
- To avoid this situation, those affected must undergo periodic Blood draws to restore iron levels, in addition to monitoring their diet.
The Risk Factors of Liver Disease
Factors that can increase the risk of liver disease are:
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Obesity
- Type 2 diabetes
- Tattoos or piercings on the body
- Injecting drugs with shared needles
- Blood transfusion before 1992
- Exposure to other people’s blood and body fluids
- Unprotected sex
- Exposure to certain chemicals or toxins
- And also, family history of liver disease.
Complications of Liver Disease
Complications of liver disease are variable, depending on the cause of the liver problems. Untreated liver disease can progress to liver failure, a life-threatening illness.
How to Prevent Liver Disease?
Drink alcohol in moderation. For healthy adults, drinking in moderation means drinking a day for women and up to two drinks a day for men.
Heavy or high-risk alcohol use is defined as more than eight drinks a week for women and more than 15 drinks a week for men.
1. Avoid Risky Behaviors
- Use a condom during sex. If you get tattoos or body piercings, choose the place well; above all, cleaning and security measures.
- And also, get help if you use illicit drugs intravenously and don’t share needles to inject drugs.
2. Get Vaccinated
- If you are at higher risk or have already infected with the hepatitis virus, talk to your doctor getting vaccinated against hepatitis A and B.
3. Use Medications Wisely
- Take prescription and over-the-counter medications only when you need them and in the recommended doses. Don’t mix drugs with alcohol.
- And also, check with your doctor before mixing herbal supplements or prescription or over-the-counter medications.
4. Avoid contact with the Blood
- Hepatitis viruses can spread by accidental needle sticks or improper cleaning of Blood or other body fluids.
5. Keep your Food Safe
- And also, wash your hands well before eating or preparing food.
- If you are travelling to a developing country, use bottled water for drinking, wash your hands, and brush your teeth.
6. Be careful with Sprinklers
- Make sure to use these products in a well-ventilated area and wear a mask when spraying insecticides, fungicides, paint, and other toxic chemicals.
- Always follow the manufacturer’s recommendations.
7. Protect the Skin
- When using insecticides and other toxic chemicals, wear gloves, long sleeves, a hat, and a mask, so the substances absorb through your skin.
- And also, keep a healthy weight. Obesity can lead to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Diagnosis of Liver Disease
Discovering the cause and extent of liver injury is essential to guide treatment. Your doctor will likely start with a medical history and a thorough physical exam.
The doctor may recommend the following:
Blood Test: A battery of blood tests known as liver function tests can diagnose liver disease. Other blood tests may do to look for genetic conditions or specific liver problems.
Imaging Tests: An ultrasound, CT scan, and MRI can show liver damage.
Study of a Tissue Sample: Removing a tissue sample (biopsy) from the liver can help diagnose liver disease and look for liver damage signs. And also, liver biopsy usually uses a long needle inserted through the skin to remove a tissue sample sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Treatment of Liver Disease
- Treatment of liver disease depends on the diagnosis.
- Some liver problems can treat with lifestyle modifications, such as stopping alcohol consumption or losing weight, usually as part of a medical program that includes careful liver function monitoring.
- Other liver problems can be treated with medicine or may require surgery.
- And also, treatment of liver disease that leads to or has ultimately led to liver failure may require a liver transplant. There are many stage 4 liver cancer trials being performed that may help us find a cure for the disease in future.
When to See the Doctor
Make an appointment with your doctor if you have persistent symptoms or signs that worry you. Seek immediate medical attention if you have abdominal pain so severe that you cannot sit still.
Conclusion
Many liver diseases are manageable if you catch them early. Left untreated, however, they can cause permanent damage.
If you have any liver problem symptoms or are at risk of developing one, make sure to check in with your healthcare provider for routine checkups and testing, if needed.
Also Read: CrossFit – Definition, Benefits, Advantages, Types of Workouts, and More